A film – also called a movie, motion picture, moving picture, picture, photoplay or (slang) flick – is a work of visual art that simulates experiences and otherwise communicates ideas, stories, perceptions, feelings, beauty, or atmosphere through the use of moving images. These images are generally accompanied by sound and, more rarely, other sensory stimulations.[1] The word "cinema", short for cinematography, is often used to refer to filmmaking and the film industry, and the art form that is the result of it.
Recording and transmission of the film
The moving images of a film are created by photographing actual scenes with a motion-picture camera, by photographing drawings or miniature models using traditional animation techniques, by means of CGI and computer animation, or by a combination of some or all of these techniques, and other visual effects.
Before the introduction of digital production, a series of still images were recorded on a strip of chemically sensitized celluloid (photographic film stock), usually at a rate of 24 frames per second. The images are transmitted through a movie projector at the same rate as they were recorded, with a Geneva drive ensuring that each frame remains still during its short projection time. A rotating shutter causes stroboscopic intervals of darkness, but the viewer does not notice the interruptions due to flicker fusion. The apparent motion on the screen is the result of the fact that the visual sense cannot discern the individual images at high speeds, so the impressions of the images blend with the dark intervals and are thus linked together to produce the illusion of one moving image. An analogous optical soundtrack (a graphic recording of the spoken words, music and other sounds) runs along a portion of the film exclusively reserved for it, and was not projected.
Contemporary films are usually fully digital through the entire process of production, distribution, and exhibition.
Etymology and alternative terms
The name "film" originally referred to the thin layer of photochemical emulsion[2] on the celluloid strip that used to be the actual medium for recording and displaying motion pictures.
Many other terms exist for an individual motion-picture, including "picture", "picture show", "moving picture", "photoplay", and "flick". The most common term in the United States is "movie", while in Europe, "film" is preferred. Archaic terms include "animated pictures" and "animated photography".
"Flick" is, in general a slang term, first recorded in 1926. It originates in the verb flicker, owing to the flickering appearance of early films.[3]
Common terms for the field, in general, include "the big screen", "the silver screen", "the movies", and "cinema"; the last of these is commonly used, as an overarching term, in scholarly texts and critical essays. In the early years, the word "sheet" was sometimes used instead of "screen".
History
Precursors
The art of film has drawn on several earlier traditions in fields such as oral storytelling, literature, theatre and visual arts. Forms of art and entertainment that had already featured moving or projected images include:
- shadowgraphy, probably used since prehistoric times
- camera obscura, a natural phenomenon that has possibly been used as an artistic aid since prehistoric times
- shadow puppetry, possibly originated around 200 BCE in Central Asia, India, Indonesia or China
- The magic lantern, developed in the 1650s. The multi-media phantasmagoria shows that magic lanterns were popular from 1790 throughout the first half of the 19th century and could feature mechanical slides, rear projection, mobile projectors, superimposition, dissolving views, live actors, smoke (sometimes to project images upon), odors, sounds and even electric shocks.
Before celluloid

The stroboscopic animation principle was introduced in 1833 with the stroboscopic disc (better known as the phénakisticope) and later applied in the zoetrope (since 1866), the flip book (since 1868), and the praxinoscope (since 1877), before it became the basic principle for cinematography.
Experiments with early phénakisticope-based animation projectors were made at least as early as 1843 and publicly screened in 1847. Jules Duboscq marketed phénakisticope projection systems in France from c. 1853 until the 1890s.
Photography was introduced in 1839, but initially photographic emulsions needed such long exposures that the recording of moving subjects seemed impossible. At least as early as 1844, photographic series of subjects posed in different positions were created to either suggest a motion sequence or document a range of different viewing angles. The advent of stereoscopic photography, with early experiments in the 1840s and commercial success since the early 1850s, raised interest in completing the photographic medium with the addition of means to capture colour and motion. In 1849, Joseph Plateau published about the idea to combine his invention of the phénakisticope with the stereoscope, as suggested to him by stereoscope inventor Charles Wheatstone, and to use photographs of plaster sculptures in different positions to be animated in the combined device. In 1852, Jules Duboscq patented such an instrument as the "Stéréoscope-fantascope, ou Bïoscope", but he only marketed it very briefly, without success. One Bïoscope disc with stereoscopic photographs of a machine is in the Plateau collection of Ghent University, but no instruments or other discs have yet been found.
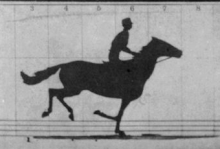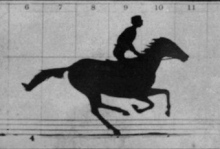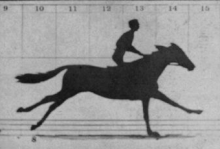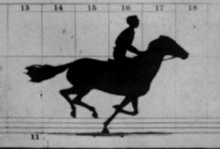
By the late 1850s the first examples of instantaneous photography came about and provided hope that motion photography would soon be possible, but it took a few decades before it was successfully combined with a method to record series of sequential images in real-time. In 1878, Eadweard Muybridge eventually managed to take a series of photographs of a running horse with a battery of cameras in a line along the track and published the results as The Horse in Motion on cabinet cards. Muybridge, as well as Étienne-Jules Marey, Ottomar Anschütz and many others, would create many more chronophotography studies. Muybridge had the contours of dozens of his chronophotographic series traced onto glass discs and projected them with his zoopraxiscope in his lectures from 1880 to 1895.

Anschütz made his first instantaneous photographs in 1881. He developed a portable camera that allowed shutter speeds as short as 1/1000 of a second in 1882. The quality of his pictures was generally regarded to be much higher than that of the chronophotography works Muybridge and Étienne-Jules Marey.[4] In 1886, Anschütz developed the Electrotachyscope, an early device that displayed short motion picture loops with 24 glass plate photographs on a 1.5 meter wide rotating wheel that was hand-cranked to the speed of circa 30 frames per second. Different versions were shown at many international exhibitions, fairs, conventions and arcades from 1887 until at least 1894. Starting in 1891, some 152 examples of a coin-operated peep-box Electrotachyscope model were manufactured by Siemens & Halske in Berlin and sold internationally.[5][4] Nearly 34,000 people paid to see it at the Berlin Exhibition Park in summer 1892. Others saw it in London or at the 1893 Chicago World's Fair.On 25 November 1894, Anschütz introduced a Electrotachyscope projector with a 6x8 meter screening in Berlin. Between 22 February and 30 March 1895, a total of circa 7,000 paying customers came to view a 1.5-hour show of some 40 scenes at a 300-seat hall in the old Reichstag building in Berlin.[6]
Émile Reynaud already mentioned the possibility of projecting the images of the Praxinoscope in his 1877 patent application. He presented a praxinoscope projection device at the Société française de photographie on 4 June 1880, but did not market his praxinoscope a projection before 1882. He then further developed the device into the Théâtre Optique which could project longer sequences with separate backgrounds, patented in 1888. He created several movies for the machine by painting images on hundreds of gelatin plates that were mounted into cardboard frames and attached to a cloth band. From 28 October 1892 to March 1900 Reynaud gave over 12,800 shows to a total of over 500,000 visitors at the Musée Grévin in Paris.
First motion pictures

By the end of the 1880s, the introduction of lengths of celluloid photographic film and the invention of motion picture cameras, which could photograph a rapid sequence of images using only one lens, allowed action to be captured and stored on a single compact reel of film.
Movies were initially shown publicly to one person at a time through "peep show" devices such as the Electrotachyscope, Kinetoscope and the Mutoscope. Not much later, exhibitors managed to project films on large screens for theatre audiences.
The first public screenings of films at which admission was charged were made in 1895 by the American Woodville Latham and his sons, using films produced by their Eidoloscope company,[7] by the Skladanowsky brothers and by the – arguably better known – French brothers Auguste and Louis Lumière with ten of their own productions.[citation needed] Private screenings had preceded these by several months, with Latham's slightly predating the others´s.[citation needed]
Early evolution

The earliest films were simply one static shot that showed an event or action with no editing or other cinematic techniques. Typical films showed employees leaving a factory gate, people walking in the street, and the view from the front of a trolley as it traveled a city's Main Street. According to legend, when a film showed a locomotive at high speed approaching the audience, the audience panicked and ran from the theater. Around the turn of the 20th century, films started stringing several scenes together to tell a story. (The filmmakers who first put several shots or scenes discovered that, when one shot follows another, that act establishes a relationship between the content in the separate shots in the minds of the viewer. It is this relationship that makes all film storytelling possible. In a simple example, if a person is shown looking out a window, whatever the next shot shows, it will be regarded as the view the person was seeing.) Each scene was a single stationary shot with the action occurring before it. The scenes were later broken up into multiple shots photographed from different distances and angles. Other techniques such as camera movement were developed as effective ways to tell a story with film. Until sound film became commercially practical in the late 1920s, motion pictures were a purely visual art, but these innovative silent films had gained a hold on the public imagination. Rather than leave audiences with only the noise of the projector as an accompaniment, theater owners hired a pianist or organist or, in large urban theaters, a full orchestra to play music that fit the mood of the film at any given moment. By the early 1920s, most films came with a prepared list of sheet music to be used for this purpose, and complete film scores were composed for major productions.
The rise of European cinema was interrupted by the outbreak of World War I, while the film industry in the United States flourished with the rise of Hollywood, typified most prominently by the innovative work of D. W. Griffith in The Birth of a Nation (1915) and Intolerance (1916). However, in the 1920s, European filmmakers such as Eisenstein, F. W. Murnau and Fritz Lang, in many ways inspired by the meteoric wartime progress of film through Griffith, along with the contributions of Charles Chaplin, Buster Keaton and others, quickly caught up with American film-making and continued to further advance the medium.
Sound
In the 1920s, the development of electronic sound recording technologies made it practical to incorporate a soundtrack of speech, music and sound effects synchronized with the action on the screen.[citation needed] The resulting sound films were initially distinguished from the usual silent "moving pictures" or "movies" by calling them "talking pictures" or "talkies."[citation needed] The revolution they wrought was swift. By 1930, silent film was practically extinct in the US and already being referred to as "the old medium."[citation needed]
The evolution of sound in cinema began with the idea of combining moving images with existing phonograph sound technology. Early sound-film systems, such as Thomas Edison's Kinetoscope and the Vitaphone used by Warner Bros., laid the groundwork for synchronized sound in film. The Vitaphone system, produced alongside Bell Telephone Company and Western Electric, faced initial resistance due to expensive equipping costs, but sound in cinema gained acceptance with movies like Don Juan (1926) and The Jazz Singer (1927).[8]
American film studios, while Europe standardized on Tobis-Klangfilm and Tri-Ergon systems. This new technology allowed for greater fluidity in film, giving rise to more complex and epic movies like King Kong (1933).[9]
As the television threat emerged in the 1940s and 1950s, the film industry needed to innovate to attract audiences. In terms of sound technology, this meant the development of surround sound and more sophisticated audio systems, such as Cinerama's seven-channel system. However, these advances required a large number of personnel to operate the equipment and maintain the sound experience in theaters.[9]
In 1966, Dolby Laboratories introduced the Dolby A noise reduction system, which became a standard in the recording industry and eliminated the hissing sound associated with earlier standardization efforts. Dolby Stereo, a revolutionary surround sound system, followed and allowed cinema designers to take acoustics into consideration when designing theaters. This innovation enabled audiences in smaller venues to enjoy comparable audio experiences to those in larger city theaters.[10]
Today, the future of sound in film remains uncertain, with potential influences from artificial intelligence, remastered audio, and personal viewing experiences shaping its development.[11][12] However, it is clear that the evolution of sound in cinema has been marked by continuous innovation and a desire to create more immersive and engaging experiences for audiences.
Color
A significant technological advancement in film was the introduction of "natural color," where color was captured directly from nature through photography, as opposed to being manually added to black-and-white prints using techniques like hand-coloring or stencil-coloring.[13][14] Early color processes often produced colors that appeared far from "natural".[15] Unlike the rapid transition from silent films to sound films, color's replacement of black-and-white happened more gradually.[16]
The crucial innovation was the three-strip version of the Technicolor process, first used in animated cartoons in 1932.[17][18] The process was later applied to live-action short films, specific sequences in feature films, and finally, for an entire feature film, Becky Sharp, in 1935.[19] Although the process was expensive, the positive public response, as evidenced by increased box office revenue, generally justified the additional cost.[13] Consequently, the number of films made in color gradually increased year after year.[20][21]




Post a Comment